Partial Discharge
What is Partial Discharge?
“A localized electrical discharge that only partially bridges the insulation between conductors and which can or cannot occur adjacent to a conductor” quoted from IEC60270 verbatim.
Why it occurs?
When voltage stress exceeds a certain maximum limit of breakdown for that portion of the insulation, partial discharge occurs and continues to happen as long as the excitation voltage is greater than the inception voltage
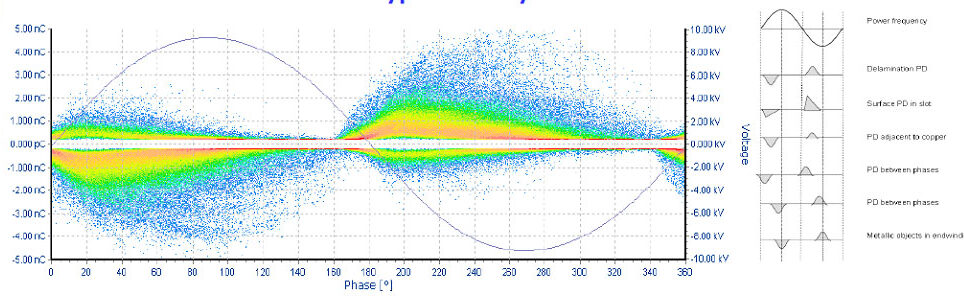
What are different types of partial discharges?
It depends upon asset, rated voltage, insulation type, shape of conductors, proximity to other phases/ground
- Corona – discharges to air
- Floating Electrode – metal to metal
- Voids – gaps in solid insulation or cavities as well as gas bubbles in liquid insulation
- Surface Discharge – tracking on the outside surface of insulation traveling towards other conductors or ground
- Partial Discharges – conductive particles contaminate insulation medium
PD Detection
PD can be detected using the following non-conventional techniques in various electrical assets:
- Acoustic Emissions (AE)
- Airborne – ultrasonic microphone 40kHz center frequency
- Contact Probe – broad range 20kHz -300 Khz (PD in oil or SF6 gas) Electromagnetic –
- RFI/UHF Ultra-High Frequency 100 MHz-1 GHz
- TEV Transient Earth Voltage 1 MHz-100 MHz
- HFCT High-Frequency Current Transformer 500kHz-50MHz
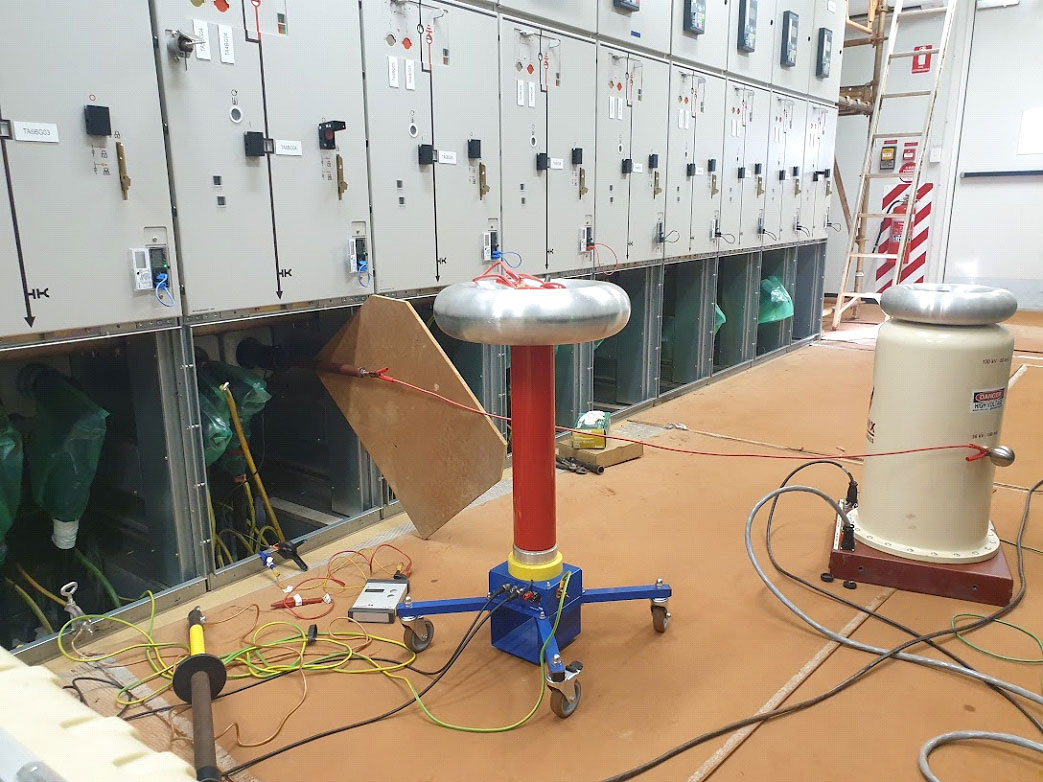

Sigma Power offers following PD Services.
- Offline and Online Partial Discharge Measurement of Rotating Machines.
- Offline and Online Partial Discharge Measurement of Power Cables.
- Offline and Online Partial Discharge Measurement of Switch Boards.
- Offline and Online Partial Discharge Measurement of Transformers.
- Online Partial Discharge Survey of AIS/GIS Substations.
- Corona Survey
- Permanent Online Partial Discharge monitoring system




 A Tasmea Company
A Tasmea Company
 www.tasmea.com.au
www.tasmea.com.au